Docker Compose Deployment
This guide shows how to deploy Hatchet using Docker Compose for a production-ready deployment. If you’d like to get up and running quickly, you can also deploy Hatchet using the hatchet-lite image following the tutorial here: Hatchet Lite Deployment.
Quickstart
Prerequisites
This deployment requires Docker installed locally to work.
Create files
We will be creating 2 files in the root of your repository:
- docker-compose.yml
- Caddyfile
version: "3.8"
services:
postgres:
image: postgres:15.6
command: postgres -c 'max_connections=200'
restart: always
hostname: "postgres"
environment:
- POSTGRES_USER=hatchet
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=hatchet
- POSTGRES_DB=hatchet
ports:
- "5435:5432"
volumes:
- hatchet_postgres_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD-SHELL", "pg_isready -d hatchet -U hatchet"]
interval: 10s
timeout: 10s
retries: 5
start_period: 10s
rabbitmq:
image: "rabbitmq:3-management"
hostname: "rabbitmq"
ports:
- "5673:5672" # RabbitMQ
- "15673:15672" # Management UI
environment:
RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER: "user"
RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS: "password"
volumes:
- "hatchet_rabbitmq_data:/var/lib/rabbitmq"
- "hatchet_rabbitmq.conf:/etc/rabbitmq/rabbitmq.conf" # Configuration file mount
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "rabbitmqctl", "status"]
interval: 10s
timeout: 10s
retries: 5
migration:
image: ghcr.io/hatchet-dev/hatchet/hatchet-migrate:latest
environment:
DATABASE_URL: "postgres://hatchet:hatchet@postgres:5432/hatchet"
depends_on:
postgres:
condition: service_healthy
setup-config:
image: ghcr.io/hatchet-dev/hatchet/hatchet-admin:latest
command: /hatchet/hatchet-admin quickstart --skip certs --generated-config-dir /hatchet/config --overwrite=false
environment:
DATABASE_URL: "postgres://hatchet:hatchet@postgres:5432/hatchet"
SERVER_TASKQUEUE_RABBITMQ_URL: amqp://user:password@rabbitmq:5672/
SERVER_AUTH_COOKIE_DOMAIN: localhost:8080
SERVER_AUTH_COOKIE_INSECURE: "t"
SERVER_GRPC_BIND_ADDRESS: "0.0.0.0"
SERVER_GRPC_INSECURE: "t"
SERVER_GRPC_BROADCAST_ADDRESS: localhost:7077
volumes:
- hatchet_certs:/hatchet/certs
- hatchet_config:/hatchet/config
depends_on:
migration:
condition: service_completed_successfully
rabbitmq:
condition: service_healthy
postgres:
condition: service_healthy
hatchet-engine:
image: ghcr.io/hatchet-dev/hatchet/hatchet-engine:latest
command: /hatchet/hatchet-engine --config /hatchet/config
restart: on-failure
depends_on:
setup-config:
condition: service_completed_successfully
migration:
condition: service_completed_successfully
ports:
- "7077:7070"
environment:
DATABASE_URL: "postgres://hatchet:hatchet@postgres:5432/hatchet"
SERVER_GRPC_BIND_ADDRESS: "0.0.0.0"
SERVER_GRPC_INSECURE: "t"
volumes:
- hatchet_certs:/hatchet/certs
- hatchet_config:/hatchet/config
hatchet-api:
image: ghcr.io/hatchet-dev/hatchet/hatchet-api:latest
command: /hatchet/hatchet-api --config /hatchet/config
restart: on-failure
depends_on:
setup-config:
condition: service_completed_successfully
migration:
condition: service_completed_successfully
environment:
DATABASE_URL: "postgres://hatchet:hatchet@postgres:5432/hatchet"
volumes:
- hatchet_certs:/hatchet/certs
- hatchet_config:/hatchet/config
hatchet-frontend:
image: ghcr.io/hatchet-dev/hatchet/hatchet-frontend:latest
caddy:
image: caddy:2.7.6-alpine
ports:
- 8080:8080
volumes:
- ./Caddyfile:/etc/caddy/Caddyfile
volumes:
hatchet_postgres_data:
hatchet_rabbitmq_data:
hatchet_rabbitmq.conf:
hatchet_config:
hatchet_certs:http://localhost:8080 {
handle /api/* {
reverse_proxy hatchet-api:8080
}
handle /* {
reverse_proxy hatchet-frontend:80
}
}Get Hatchet up and running
To start the services, run the following command in the root of your repository:
docker compose upWait for the hatchet-engine and hatchet-api services to start.
Accessing Hatchet
Once the Hatchet instance is running, you can access the Hatchet UI at http://localhost:8080.
By default, a user is created with the following credentials:
Email: admin@example.com
Password: Admin123!!Generate a .env file
You can generate a .env file as follows:
cat <<EOF > .env
HATCHET_CLIENT_TOKEN="$(docker compose run --no-deps setup-config /hatchet/hatchet-admin token create --config /hatchet/config --tenant-id 707d0855-80ab-4e1f-a156-f1c4546cbf52 | xargs)"
HATCHET_CLIENT_TLS_STRATEGY=none
EOFYou can also generate an API token by logging in and navigating to the “General” settings page, clicking on the “API Tokens” tab, and then clicking “Create API Token”.
Run your first worker
Make sure you have the following dependencies installed:
pip install python-dotenv
pip install hatchet-sdkWe are using python-dotenv to load the environment variables from a .env file. This isn’t required, and you can use your own method to load environment variables.
Create a worker.py file with the following contents:
from hatchet_sdk import Hatchet
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
hatchet = Hatchet(debug=True)
@hatchet.workflow(name="first-python-workflow",on_events=["user:create"])
class MyWorkflow:
@hatchet.step()
def step1(self, context):
return {
"result": "success"
}
if __name__ == "__main__":
worker = hatchet.worker('first-worker')
worker.register_workflow(MyWorkflow())
worker.start()Open a new terminal and start the worker with:
python3 worker.pyRun your first workflow
The worker is now running and listening for steps to execute. You should see your first worker registered in the Workers tab of the Hatchet dashboard:
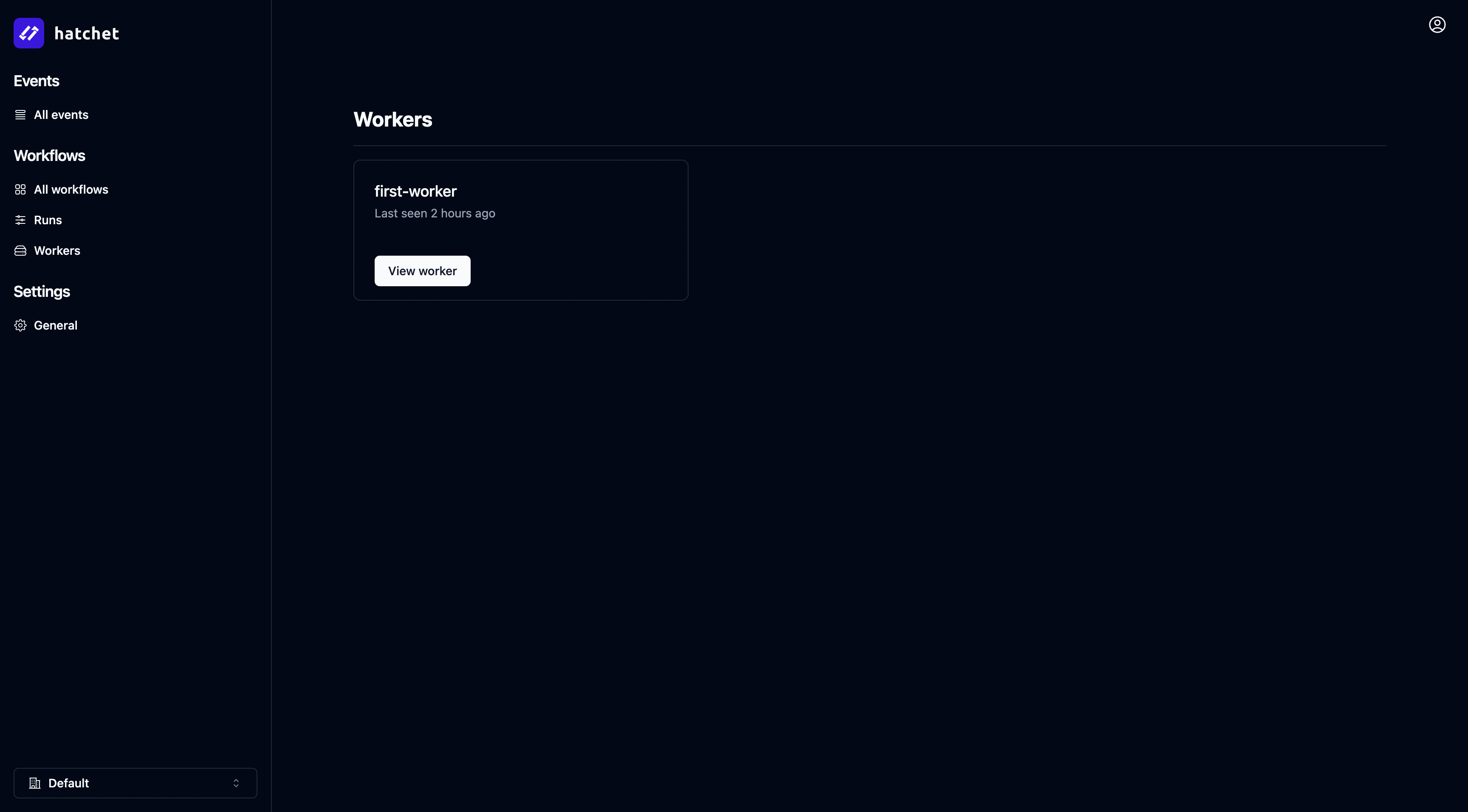
You can now trigger your first workflow by navigating to the Workflows tab, selecting your workflow, and clicking the top right “Trigger workflow” button:
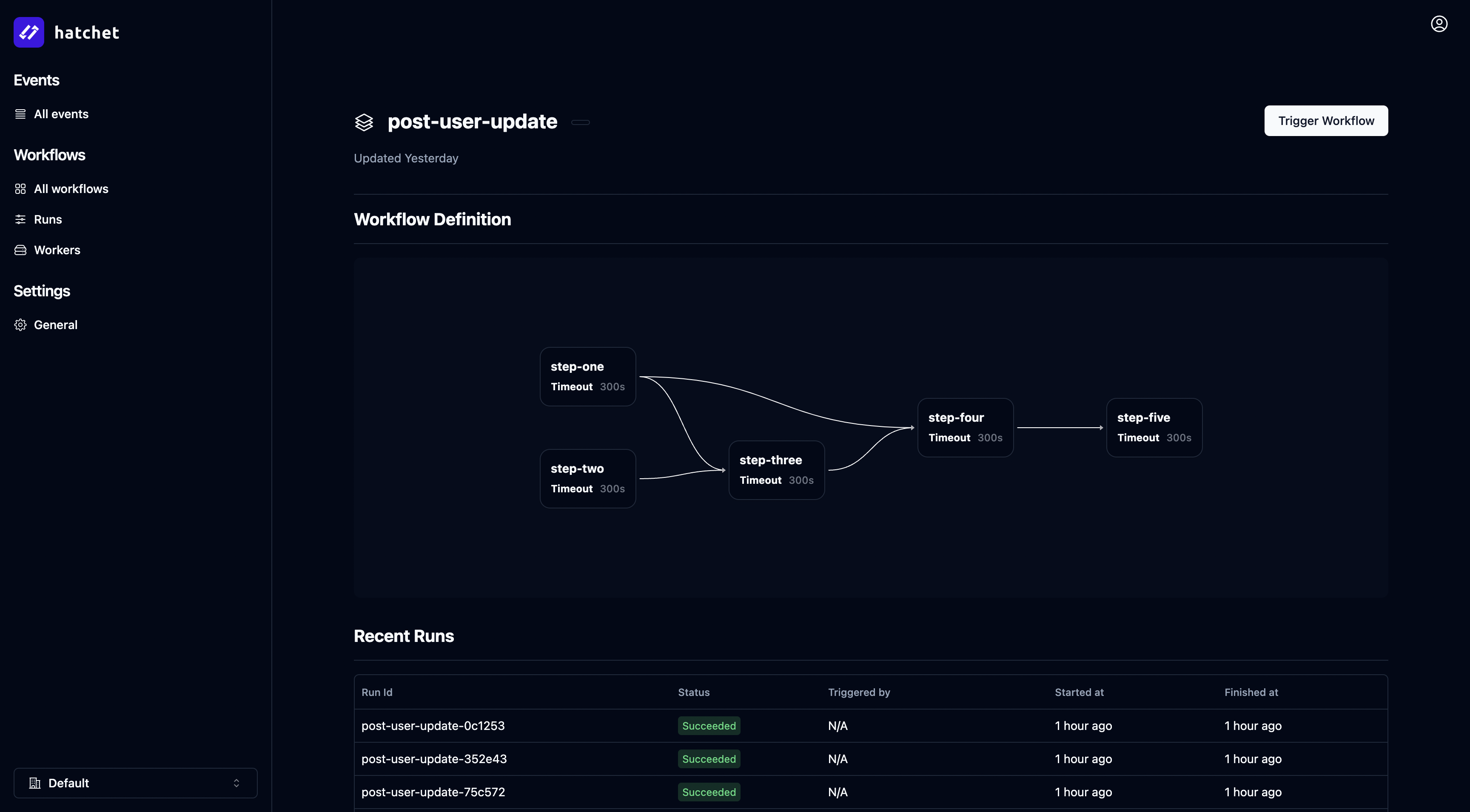
That’s it! You’ve successfully deployed Hatchet and run your first workflow.
Connecting to the engine from within Docker
If you’re also running your worker application inside of docker-compose, you should modify the SERVER_GRPC_BROADCAST_ADDRESS environment variable in the setup-config service to use host.docker.internal as the hostname. For example:
SERVER_GRPC_BROADCAST_ADDRESS: "host.docker.internal:7077"Note: modifying the GRPC broadcast address or server URL will require re-issuing an API token.