Python SDK
This is the Hatchet Python SDK reference. On this page, we’ll get you up and running with a Python worker. This guide assumes that you already have a Hatchet engine instance running. If you don’t, you can:
- Sign up on Hatchet Cloud
- Self-host Hatchet
If you run into any issues, please file an issue on the Hatchet Python SDK GitHub repository.
Installation
If using pip, you can run:
pip install hatchet-sdkIf using poetry:
poetry add hatchet-sdkGenerate a Token
Navigate to your Hatchet dashboard and navigate to your settings tab. You should see a section called “API Keys”. Click “Create API Key”, input a name for the key and copy the key. Then set the following environment variables:
HATCHET_CLIENT_TOKEN="<your-api-key>"You may need to set additional environment variables depending on your self-hosted configuration. The Hatchet clients default to SSL by default, but to disable this you can set:
HATCHET_CLIENT_TLS_STRATEGY=noneRun your first worker
Make sure you’ve set the HATCHET_CLIENT_TOKEN environment variable via export HATCHET_CLIENT_TOKEN="<your-api-key>". Then copy and run the following Python script via python worker.py:
import asyncio
from hatchet_sdk import Context, Hatchet
hatchet = Hatchet(debug=True)
@hatchet.workflow(on_events=["user:create"])
class Workflow:
def __init__(self):
self.my_value = "test"
@hatchet.step(timeout="2s")
async def step1(self, context: Context):
context.refresh_timeout("5s")
print("started step1")
await asyncio.sleep(1)
print("finished step1")
return {"test": "test"}
@hatchet.step(parents=["step1"], timeout="4s")
async def step2(self, context):
print("started async step2")
await asyncio.sleep(1)
print("finished step2")
async def main():
worker = hatchet.worker("first-worker", max_runs=4)
worker.register_workflow(Workflow())
await worker.async_start()
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())Run your first workflow
The worker is now running and listening for steps to execute. You should see your first worker registered in the Workers tab of the Hatchet dashboard:
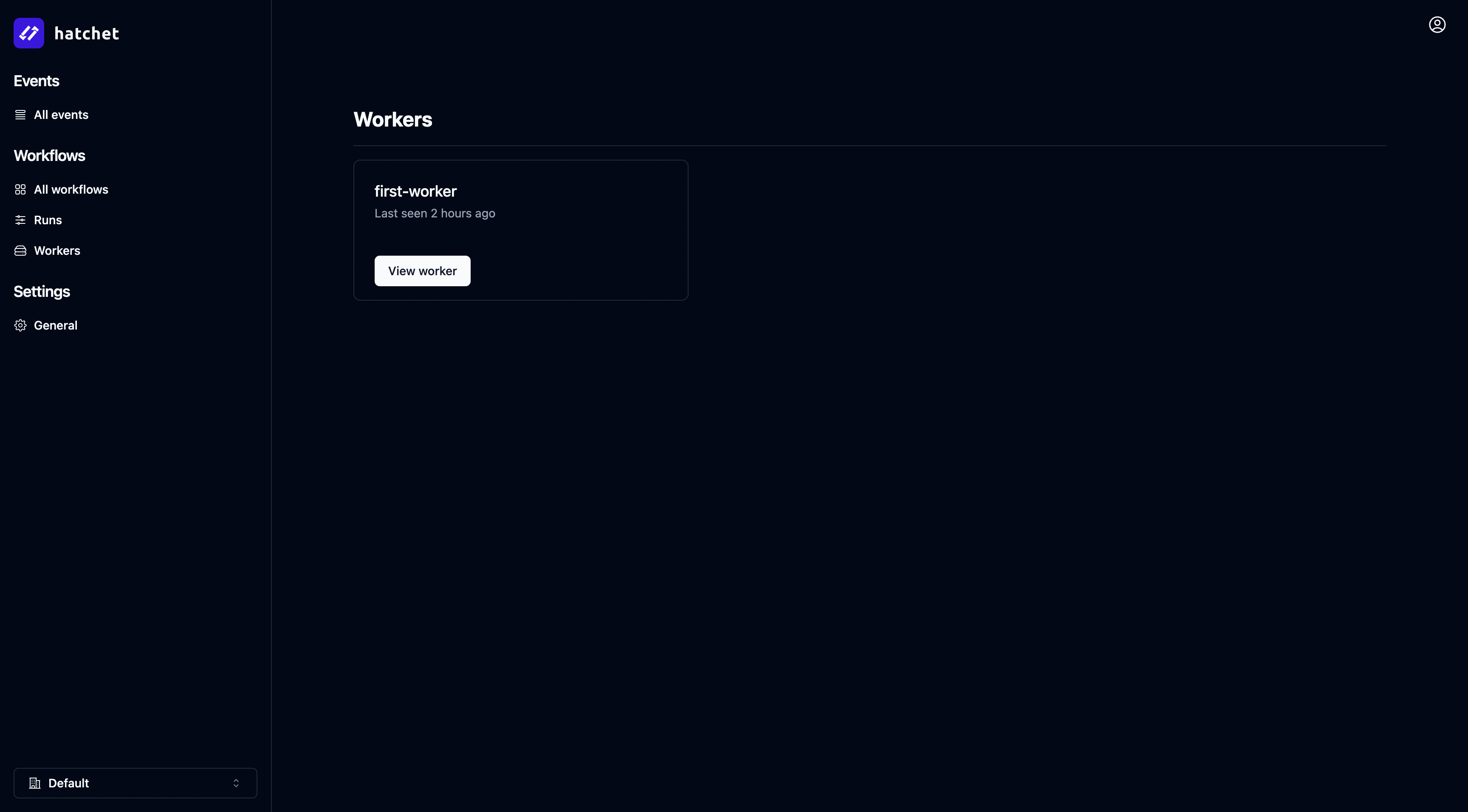
You can now trigger your first workflow by navigating to the Workflows tab, selecting your workflow, and clicking the top right “Trigger workflow” button:
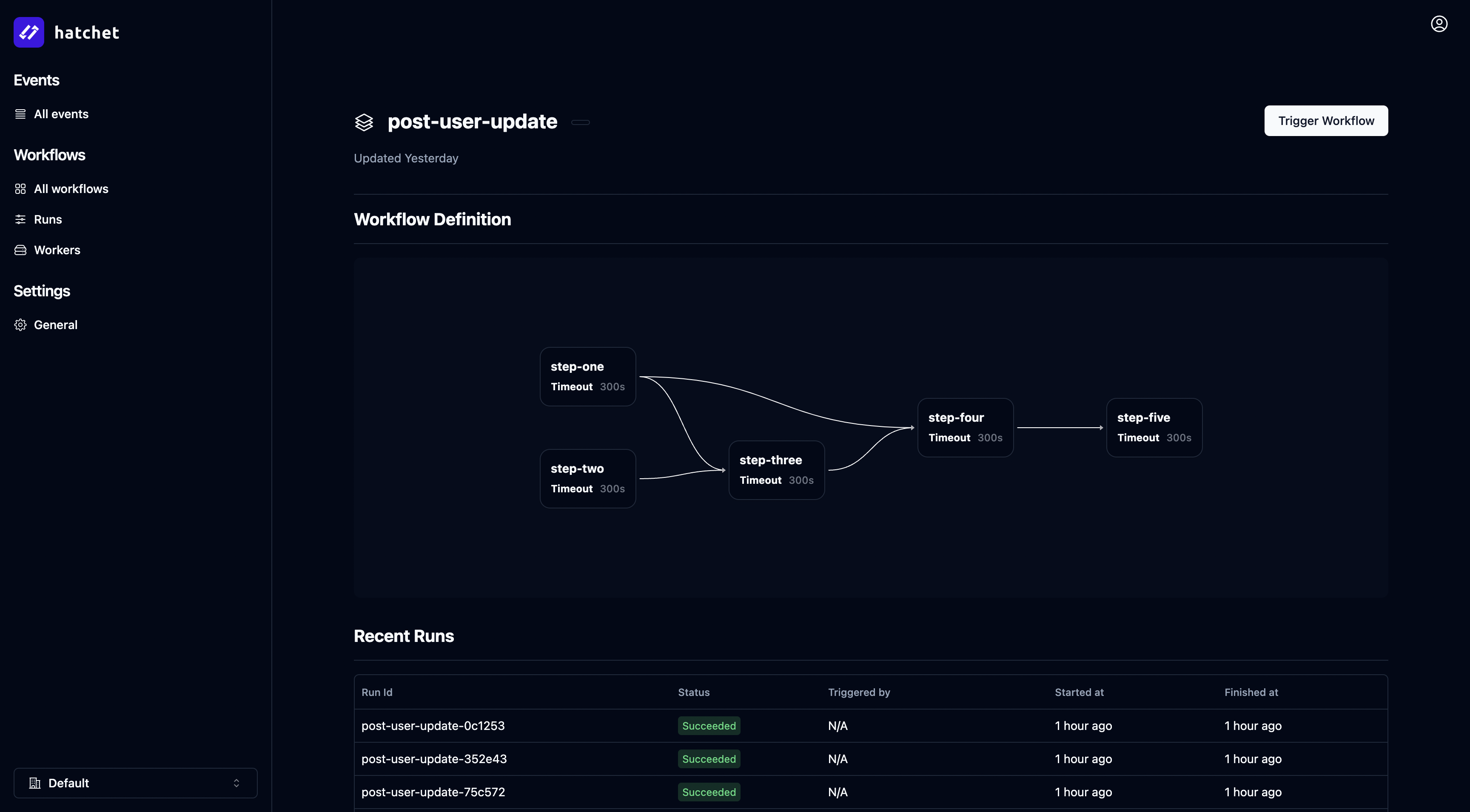
That’s it! You’ve successfully deployed Hatchet and run your first workflow.
Next Steps
Congratulations on running your first workflow!
To test out some more complicated examples, check out the Hatchet Python Quickstart.